
If there isn't enough space to store them (that is, max(p1 - s1, p2 - s2) < min(38, precision) - scale), the scale is reduced to provide enough space for the integral part. In addition and subtraction operations, we need max(p1 - s1, p2 - s2) places to store the integral part of the decimal number. In some cases such as multiplication or division, scale factor isn't reduced, to maintain decimal precision, although the overflow error can be raised.
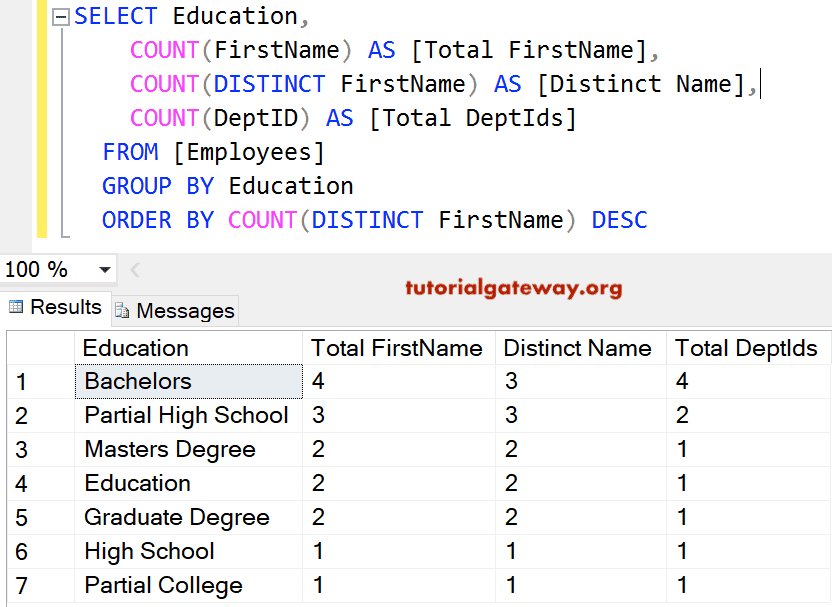
When a result precision is greater than 38, it's reduced to 38, and the corresponding scale is reduced to try to prevent truncating the integral part of a result. Operationġ The result precision and scale have an absolute maximum of 38. Similarly, min(a, b) indicates to take the smaller value of a or b. The function max(a, b) indicates to take the greater value of a or b. The precision and scale for any expression that isn't decimal is the precision and scale defined for the data type of the expression. The operand expressions are denoted as expression e1, with precision p1 and scale s1, and expression e2, with precision p2 and scale s2.

The int data type has a precision of 10, a length of 4, and a scale of 0. For example, an int data type can hold 10 digits, is stored in 4 bytes, and doesn't accept decimal points.
The length for binary, varbinary, and image data types is the number of bytes. For nvarchar and nchar, the length of the character string is the number of byte-pairs. For varchar and char, the length of a character string is the number of bytes. Length for a numeric data type is the number of bytes that are used to store the number. In SQL Server, the default maximum precision of numeric and decimal data types is 38. For example, the number 123.45 has a precision of 5 and a scale of 2. Scale is the number of digits to the right of the decimal point in a number. Precision is the number of digits in a number. Applies to: SQL Server Azure SQL Database Azure SQL Managed Instance Azure Synapse Analytics Analytics Platform System (PDW) SQL Endpoint in Microsoft Fabric Warehouse in Microsoft Fabric


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
